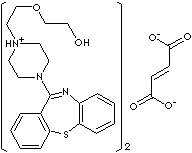
| Quetiapine, a dibenzothiazepine derivative, is an atypical antipsychotic agent
to treat psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia, hallucinations,
delusions, hostility and other bipolar disorder. It is sometimes prescribed for
other uses (off-labeled) against other disorders such as posttraumatic stress
disorder and sleep disorders. The hemifumarate salt of quetiapine is a white to
off-white crystalline powder; soluble in water, melting point 172 - 174 C;
administered orally. It is chemically described as 2-[2-(4-dibenzo [b,f]
[1,4]thiazepin-11-yl-1- piperazinyl)ethoxy] ethanol fumarate (2:1) (salt). |
The term antipsychotic refers to a group of drugs effective in the treatment of
psychosis including schizophrenic, paranoid, schizoaffective, bipolar disorder,
and other psychotic disorders. Traditional antipsychotic agents have
phenothiazine structure chemically. Phenothiazinene drugs are adrenergic
blocking agents. Their pharmacologic actions including central nervous system
depression, prolongation and potentiation of the effects of narcotic and
hypnotic drugs, hypotensive activity, and antispasmodic, antihistaminic, and
antiemetic activity. Other chemcial structures for antipsychotic drugs are
diverse, they include thioxanthene, butyrophenone, dibenzoxazepine,
dihydroindolone, benzisoxazole, and diphenylbutylpiperidine. Antipsychotic
agents bind to dopamine, histamine, muscarinic cholinergic, a-adrenergic, and
serotonin receptors. Blockade of dopaminergic transmission in various areas is known
to be responsible for their major effects such as not
only antipsychotic action by
blockade in the mesolimbic and mesocortical areas and and antiemetic effects by blockade in the chemoreceptor trigger
zone of the medulla but also extrapyramidal side effects
(dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism, and tardive dyskinesia) by blockade in the
basal ganglia and sedation and autonomic side effects (orthostatic
hypotension, blurred vision, dry mouth, nasal congestion, and constipation) by blockade of histamine, cholinergic, and adrenergic receptors.
The antipsychotic agents may be divided by chemical group and and the decreased propensity of extrapyramidal side effects
into two main groups and a new class which is being
processed.
- Typical Antipsychotic
- Chlorpromazine (CAS
#: 50-53-3,
Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Promazine (CAS
#: 58-40-2, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side
chain)
- Triflupromazine
(CAS #: 146-54-3, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Methotrimeprazine (CAS
#: 60-99-1,
Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Thioridazine (CAS
#: 50-52-2,
Phenothiazine with piperidine side chain)
- Mesoridazine (CAS
#: 5588-33-0, Phenothiazine with piperidine
side chain)
- Acetophenazine (CAS
#:2751-68-0, Phenothiazine with piperazine
side chain)
- Perphenazine (CAS
#: 58-39-9,
Phenothiazine with piperazine
side chain)
- Trifluoperazine (CAS
#: 117-89-5,
Phenothiazine with piperazine
side chain)
- Fluphenazine (CAS
#: 69-23-8,
Phenothiazine with piperazine
side chain)
- Prochlorperazine (CAS
#: 58-38-8,
Phenothiazine with piperazine
side chain)
- Chlorprothixene (CAS
#: 113-59-7 Thioxanthene)
- Thiothixene (CAS
#: 22189-31-7, Thioxanthene)
- Haloperidol (CAS
#: 52-86-8, Phenylbutylpiperadine)
- Pimozide (CAS
#:
2062-78-4, Phenylbutylpiperadine)
- Loxapine (CAS
#: 1977-10-2,
Dibenzoxazepine)
- Molindone (CAS
#: 7416-34-4, Dihydroindolone)
- Atypical
Antipsychotics
- Clozapine (CAS
#: 5786-21-0, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Olanzapine (CAS
#:
132539-06-1, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Quetiapine (CAS
#: 111974-69-7, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Ziprasidone (CAS
#: 138982-67-9, Benzisoxazole)
- Risperidone (CAS
#: 106266-06-2, Benzisoxazole)
- Partial dopamine agonists
- Aripiprazole (CAS
#: 129722-12-9, Dihydroquinolinone)
- Lithium carbonate
|